Path to Net Zero
Upstream Gas Industry Enters New Era of Emissions
The transition to a low-carbon energy future raises tough questions for the U.S. upstream natural gas industry about its environmental impacts and measures to mitigate them. The shift also threatens to end nearly 20 years of growth in gas production.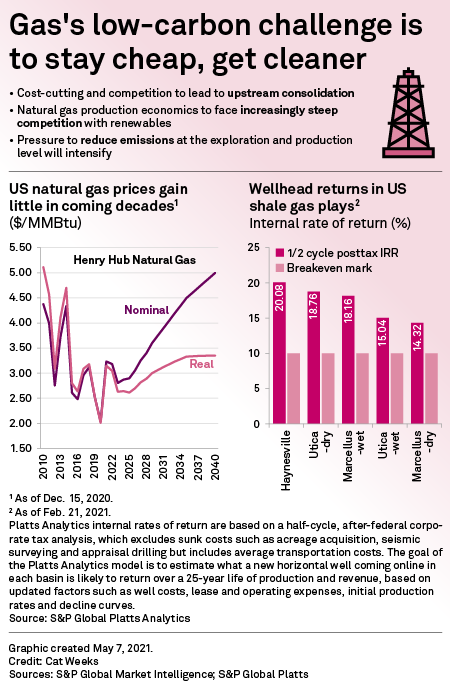
DT Midstream CEO Details Growth, Decarbonization Targets
S&P Global Market Intelligence spoke with DT Midstream CEO David Slater about the firm's plans for expansion and decarbonization. Slater said carbon capture and sequestration are primary focuses.
READ THE FULL ARTICLEEmissions-Conscious Markets Weigh on U.S. LNG's Future
The U.S. natural gas industry faces a new urgency to keep its exported LNG cargoes attractive to consumer nations that aspire to meet net-zero targets in 2050.
Read the Full ArticlePressured Gas Sector Urged to Probe Segments Across Value Chain to Cut Emissions
From production to end-use, pressure on the gas industry to curb emissions is driving companies all along the value chain to take a hard look at their operations.
Read the Full ArticleGas Could Have Role In Low-Carbon World, But Emissions Policies Critical
Natural gas could continue to play a key role in a decarbonized global economy, but there might be significant regional differences and conflicts with local decarbonization goals that could influence the future of U.S. LNG.
Read the Full Article
Energy Value Chain
'If Not Us, Who?' Cheniere Leans Into Cleaning Up Natural Gas Supply Chain
The way that Cheniere Energy Inc. responds to the emissions concerns of its customers could be a key driver for a U.S. natural gas industry that is becoming more export oriented.
A series of climate initiatives launched by Cheniere, the country's biggest LNG exporter, came on the eve of the company bringing its ninth liquefaction train online. The train will raise the company's annual export capacity to a combined 45 million tonnes per year across its two export plants in Louisiana and Texas.
Cheniere has embraced its role as a bridge to international markets that have aggressive climate policies. The company has ramped up efforts to tackle one of the most pressing risks for the gas industry: climate-warming emissions throughout the natural gas supply chain.
High-Stakes Battles Over Gas Use Take Shape
The U.S. natural gas sector faces risks and opportunities across the value chain as the energy sector accelerates toward less carbon-intensive operations. Some segments and businesses are better positioned than others to survive the shift.
Read the Full ArticleGrid-Balancing Tactics In Flux as Battery Costs Fall
Advancements in battery storage pose a significant risk to natural gas as the rapid growth of renewable power erodes market share for the fossil fuel in the decades ahead.
In independent system operator territories across the U.S., wind power has become the single largest threat to market share for gas as a cleaner power source as coal and nuclear generation retires.
Read the Full Article
Gas-Fired Generation
Gas-Fired Generation to Lose Ground In Low-Carbon Era
An accelerating transition toward a low-carbon energy future appears poised to drive a decline in natural gas-fired generation. Underpinning that transformation in the years ahead will be sustained wind and solar adoption, propelled by their falling costs and mounting policy pressure for renewable energy.
Renewables Capturing Market From Gas-Fired Generation
The accelerating transition toward a low-carbon future promises a slow decline for gas-fired power generation in the years ahead as wind and solar continue to gain traction, propelled by low costs and mounting policy pressure for adoption.
In 2020, natural gas accounted for a record 38% of total power generation in the US. By the early 2030s, its market share is now forecast to fall below 30%. Over the same decade-long period, total generation from wind and solar is expected to climb from just 11% in 2020, to more than 30% by 2030, according to a recently updated reference-case forecast from S&P Global Platts Analytics.
In the 2030s and beyond, as the energy transition unfolds, the trajectory of individual gas-fired power plants will vary widely depending upon their location and the prevailing market and policy environment.
Financing Conditions
QP to Spend $200 Million on Emissions Reduction Technology for LNG Expansion Project
Qatar Petroleum will spend $200 million on emissions reduction technology for its North Field LNG expansion project, according to the company's bond prospectus, seen by S&P Global Platts June 30.
The prospectus lists "greenhouse gas reduction measures including the installation of a CO2 capture and sequestration system, power import from solar power plants, maximization of waste heat recovery, improved machines efficiency utilizing latest available technology, and the use of ultra low NOx burners."
"These design improvements are expected to achieve an estimated 30% reduction in GHG emissions, compared to similar existing LNG facilities," it said.
The first phase of the the two-phase North Field expansion project will cost $28.75 billion -- making it one of the largest energy projects globally -- and boost Qatar's LNG production to 110 million mt/year from 77 million mt/year.
UGI to Invest More Than $1B In Renewable Gas Through 2025
Gas transportation and distribution company UGI Corp. expects to spend more than $1 billion on renewable gas investments over the next five years, executives said on the company's June 21 investor day presentation.
READ THE FULL ARTICLEMidstream Sector Must Prepare for Norms to be Upended
After a yearslong infrastructure spending and building boom, the U.S. midstream sector faces a pivotal moment as the energy transition gathers speed and political and financial barriers to new natural gas pipelines multiply.
Read the Full Article
Market Risks
G-7 Decision to Leave Natural Gas, Oil Off Table Raises Eyebrows
With much of the post-summit commentary focusing on the Group of Seven promise to phase out public financing for coal plants, the fact that world leaders omitted any mention of natural gas and oil was just as significant, some critics said after the high-level meeting concluded June 13.
Although the U.S. and other developed nations are transitioning away from coal-fired generation, natural gas continues to replace much of that capacity — a trend that will make U.S. President Joe Biden's goal to decarbonize the power sector by 2035 difficult to achieve. But the G-7 communique did not mention ending government subsidies for the oil and gas industry domestically or overseas, nor did it set a time frame for when to wean nations off such fuels.
Sun Is Setting on Shale Gas-Driven Pipeline Building Boom
As the energy transition gathers pace, mounting political and financial barriers to new natural gas pipeline infrastructure threaten to end the midstream industry's years-long spending and building boom.
Read the Full ArticleU.S. Residential-Commercial Markets Face Uncertainty
As state and local governments across the U.S. pursue increasingly aggressive carbon-reduction targets, the market risks to natural gas are mounting.
Read the Full ArticleThe energy transition is affecting the U.S. natural gas industry from burner tip back to the wellhead. Across the natural gas value chain there are risks and opportunities.
Access The Topic Page




