Recovery
India Infrastructure: Recovery Won't Be Quick
The hit to the India's infrastructure sector from COVID-19 will still be felt in 2021 even amid an economic recovery following lockdown. Credit risks are rising because of increasing debt levels and a weakening of counterparties.
Refinancing remains difficult for speculative grade-rated issuers.
Mexico Announces Second Set of Infrastructure Projects to Reactivate Economy
Mexico has announced a second set of infrastructure projects aimed at revitalizing the country's economy and aiding the state utility CFE's strategy of increasing its generation capacity.
Read the Full Article
U.S.
Updated Activity Estimates for U.S. Transportation Infrastructure Show Public Transit and Airport Operators Still Face a Long Recovery
Although general mobility is improving, S&P Global Ratings considers the recovery in activity across most U.S. transportation subsectors fragile and generally materially depressed compared with pre-pandemic levels. Based on S&P Global Ratings' analysis of various factors influencing future activity levels, transit systems and airports (and facilities supporting them, like fuel facilities, consolidated rental car facilities, and certain parking facilities) remain depressed and will take longer to recover within the U.S. transportation infrastructure sector, while future activity levels of toll road and port operators are better positioned for recovery or are well on their way. The key variables influencing S&P Global Ratings' view for 2021 and beyond are when herd immunity to COVID-19 is achieved and the reaction of governments and the traveling public to an evolving health and safety landscape.
Outlook for U.S. Not-For-Profit Transportation Infrastructure: Light at Tunnel’s End – but How Long is the Tunnel?
S&P Global Ratings' 2021 view of business conditions and credit quality across U.S. public transportation infrastructure is negative for the airport, mass transit, parking, and toll road sectors and stable for the ports and federal grant-secured sectors.
The COVID-19 pandemic and related economic impacts had a dramatic effect on credit quality in 2020 across the U.S. not-for-profit transportation portfolio: 109 ratings (36%) were downgraded by at least one notch and 88% retain a negative outlook.

Energy Transition
Hydrogen Era No Longer a Distant Mirage
This is the first of a five-part series exploring the burgeoning hydrogen economy and its rise — after decades of false dawns — to the top of the energy agenda in 2020.
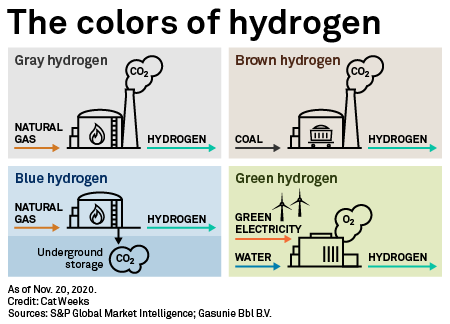
The potential future of carbon-free energy is taking shape in an unlikely place: the Texas oil patch.
For decades oil producers have stored fossil fuels in manmade caverns carved into naturally occurring salt domes, deep below the surface of the U.S. Gulf Coast. Three of these subterranean storage facilities, all in southeast Texas, also house huge volumes of hydrogen derived from natural gas. This so-called "gray hydrogen" flows through a dedicated pipeline network to major oil refineries and ammonia plants across the region, forming an essential feedstock for the global fossil fuel-based economy.
Electric Vehicles Will Contribute to Decarbonization, but Big Investments In Charging Needed
Electric vehicles are projected to comprise 40% of new car purchases by 2030 in the US, up from 2% currently, and require "substantial" power sector infrastructure investments if EV's are expected to contribute to economy-wide decarbonization.
Read the Full ArticleUK Government Needs to Invest In EV Battery Production to Meet Climate Targets
The UK government may struggle to meet its ambitious 10-point sustainability plan without investment in and the construction of home-grown battery capacity, causing unease within the industry.
Read the Full Article
Financial Infrastructure
ESG Industry Report Card: Financial Market Infrastructure Companies
The world's financial market infrastructure companies face risks but also opportunities to credit quality from the increasing focus of stakeholders on environmental, social, and governance factors.
Key Takeaways
- S&P Ratings expect social and environmental risks and opportunities will most likely emerge in the medium to long term, if at all, though what each company does in the next few years will shape them.
- FMIs have a unique opportunity to use their product expertise, large pools of liquidity, and role as standard-setters to help issuers, markets, and economies adapt to the carbon transition and climate change. Some might gain large new streams of revenue.
- S&P Ratings expect governance to continue to be the ESG factor that influences credit quality most often. Strong governance and robust ERM support our high ratings on FMIs, but their record is not perfect. As in the past, material failures in these areas could precipitate immediate negative rating actions.

Steel
China's Infrastructure Investment Push Seen Set to Boost Steel Demand in Q3
China's local government special bonds issuance, which is designed to mainly fund infrastructure projects, is expected to gather pace in August, supporting steel demand in the remainder of the third quarter and into Q4, market sources said August 6.
China issued Yuan 2.266 trillion ($326 billion) of new special bonds over January-July, leaving a balance of about Yuan 1.484 trillion ($214 billion) to be issued by year end, according to the Ministry of Finance. The ministry wants the balance to be issued in October.
Steel Demand Expected to Improve as China Plans Water Projects to Prevent Floods
A standstill in construction activities following heavy rain and massive floods in China recently dampened local steel demand in certain regions, but market watchers believe demand will benefit from water infrastructure projects worth 1.29 trillion Chinese yuan that the Chinese government recently committed to construct for long-term flood prevention.
Read the Full Article
Tech
5G Survey: Despite COVID-19 Delays, Operator Roadmaps Still Lead to 5G
Despite the negative impact on network upgrade activities caused by the COVID-19 pandemic, mobile network operators, or MNOs, remain overwhelmingly committed to 5G infrastructure buildouts and service deployments.
Key Takeaways
- According to Kagan's 2020 global 5G survey of 73 mobile operators, 38% of respondents indicated that they already offer 5G service.
- An additional 36% are planning to offer 5G services during 2021, with 16% indicating plans to do so in 2022.
- While 63% of operators said COVID-19 prompted them to slow their 5G builds, more than one third (36%) said the pandemic had either little to no effect on their 5G plans, or actually accelerated 5G network upgrades.
- Based on data Kagan has seen in both its semi-annual 5G Tracker reports, and its quarterly small cell market share reports for 2020, the impact of COVID-19 has slowed operator implementations of 5G equipment but has not come close to stopping these network upgrades outright.

Transportation
Activity Estimates For U.S Transportation Infrastructure Show Public Transit And Airports Most Vulnerable To Near-Term Rating Pressure
The COVID-19 pandemic has dramatically reshaped the global transportation industry like no other disruptive force in modern history.
Key Takeaways
- Based on S&P Global Ratings analysis of various factors influencing future activity levels for each U.S. transportation infrastructure subsector S&P Global Ratings believe the public transit and airport sectors are generally the most vulnerable to downward rating pressure in the near term.
- S&P Global Ratings current 2020 and 2021 baseline activity estimates relative to pre COVID-19 levels show annualized declines of approximately 55% and 30% for public transit; 50% and 25% for airports; 45% and 15% for parking; 25% and 10% for toll roads; and 20% and 10% for ports. However, due to the high degree of uncertainty about the rate of spread and peak of the coronavirus outbreak, the recession and their combined impacts on transportation infrastructure, S&P Global Ratings activity estimates will change as more data become available.








